Validation and the study of aflatoxin M1 contamination in milk and milk products
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.60136/bas.v10.2021.143Keywords:
Aflatoxin M1, High-performance liquid chromatography, milk and milk productAbstract
Aflatoxin M1 (AFM1) has been identified as toxic substance, which produced from the metabolism of Aflatoxin B1 (AFB1) in mammals that consumed contaminant feed. AFB1 is metabolized by enzyme in liver cells and transformed to AFM1 then excrete through mammal milk. There are both indirect and direct adverse effected to the consumer who consumed meat and milk contaminated with Aflatoxin. Continuously consumtion can be resulted in accumulation in body hence contribute to liver cancer. The Codex Alimentarius Commission has established standard of AFM1 in milk product to less than 0.5 microgram/Kilogram.
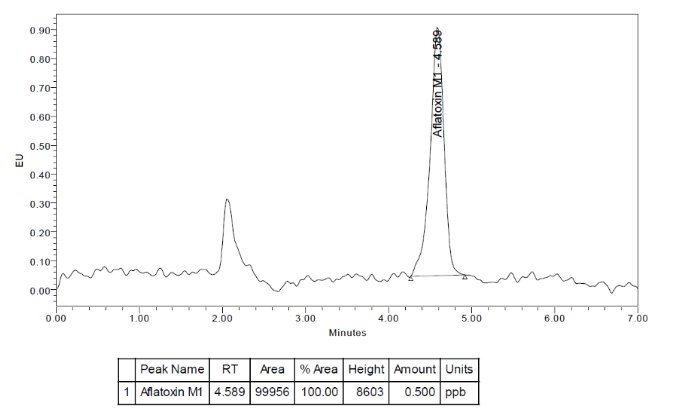
The aim of this study was to investigate the optimum condition and verification for AFM1 testing method which using HPLC. The study showed the linear correlation between the concentrations from 0.1 to 50 microgram/Liter, limit of detection (LOD) of 0.001 microgram/Liter and limit of quantitation (LOQ) of 0.004 microgram/Liter. The study also demonstrated acceptable percent recovery, precision by relative standard deviation (%RSD). The uncertainty of testing also included in this study. Animal feed samples were taken farms dairy farm in Nakorn-Rachasima and Saraburi provinces. While milk and milk products were sampled from markets in Bangkok, Nakorn-Rachasima and Saraburi provinces Results illustrated the AFM1 concentrations range from not detected to 0.0552 microgram/Kilogram.
References
Agents Classified by the IARC Monographs, Vol. 1–125, p. 15/39
American Scientific Research Journal for Engineering, Technology and Sciences (ASRJETS) (2013) Vol. 7, No. 1, p. 1-32
Badea, M., Micheli, L., Messia, M.C., Candigliota, T., Marconi, E., Mottram, T., Velasco-Garcia, M., Moscone, D., Palleschi, G., 2004. Aflatoxin M1 determination in raw milk using a flow-injection immunoassay system Analytica Chimica Acta, 520, p.141–148
Commission Regulation (EC) No 1881/2006 of 19 December 2006 setting maximum levels for certain contaminants in foodstuffs (Text with EEA relevance) (OJ L 364, 20.12.2006, p. 5)
Dragacci, S. and Fremy, J. M., 1996. Application of Immunoaffinity Column Cleanup to Aflatoxin M1 Determination and Survey in Cheese Journal of Food Protection, Vol. 59, No.9, p. 1011-1013
Dragacci, S., Grosso, F. and Gilbert, J., 2001. Immunoaffinity Column Cleanup with Liquid Chromatography for Determination of AflatoxinM1 in Liquid Milk: Collaborative Study Journal of AOAC International Vol. 84, No. 2, p. 437- 443
Food and Agriculture Organization and World Health Organization. Codex Alimentarius Commission. Agenda Item 5, CX/CF 10/4/5: FAO/WHO, March 2010, p.1-25.
General Standard for Contaminants and Toxins in Food and Feed Codex Alimentarius International Food Standards. CXS 193-1995 Amended in 2019, p.32
Hamid Mohammadi, 2011. A Review of Aflatoxin M1, Milk, and Milk Products Aflatoxins - Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, No. 19, p.397-414
Iha, M.H., Barbosa,C.B. and Favaro, R.M.D., Mary W. , 2011. Trucksess Chromatographic Method for the Determination of Aflatoxin M1 in Cheese, Yogurt, and Dairy Beverages Journal of AOAC International Vol. 94, No. 5
Iqbal, S.Z., Asi, M.R., 2013.Assessment of aflatoxin M1 in milk and milk products from Punjab, Pakistan Food Control, Vol.30, p.235-239
Muscarella, M., Magroa, S.L., Palermo, C., Centonze, D., 2007. Validation according to European Commission Decision 2002/657/EC of a confirmatory method for aflatoxin M1 in milk based on immunoaffinity columns and high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection Analytica Chimica Acta, 594, p.257–264
Nemati, M., Mehran, M.A., Hamed, P.K., Masoud, A., 2010. A survey on the occurrence of aflatoxin M1 in milk samples in Ardabil, Iran Food control, Vol. 21, p.1022-1024.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2021 Bulletin of Applied Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.









