Determination of chloride in admixtures and aggregates for concrete by flow injection potentiometry
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.60136/bas.v4.2015.289Keywords:
Flow injection, Potentiometry, Chloride, Concrete, Hydrodynamic injectionAbstract
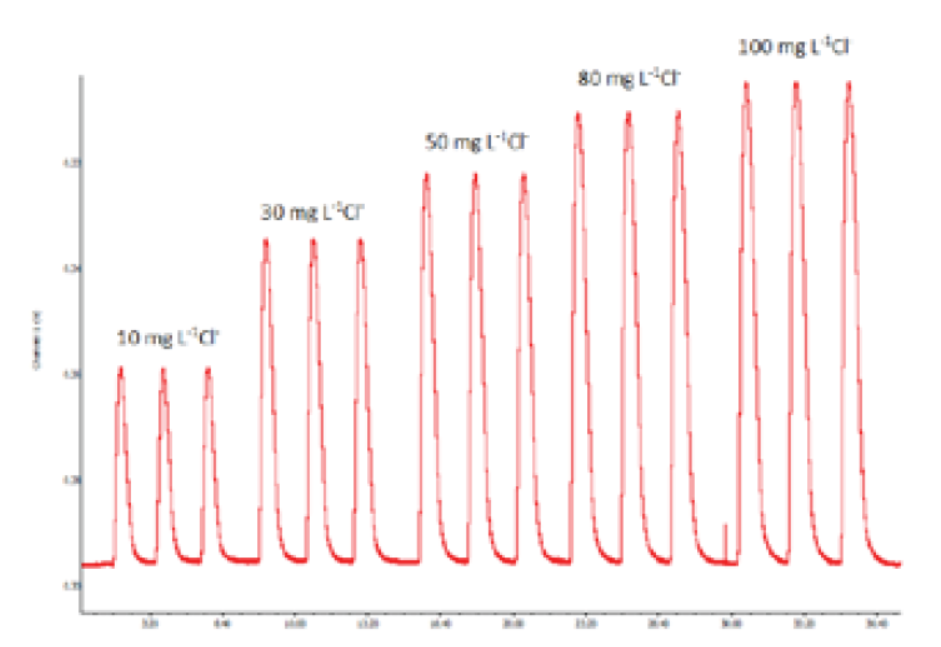
A simple flow injection system using three 3-way solenoid valves as an electric control injection valve and with a simple home-made chloride ISE based on Ag/AgCl wire as a sensor for determination of chloride in admixtures and aggregates for cement has been developed. A liquid sample or an extract was injected into a water carrier stream which was then merged with 0.1 M KNO3 stream and flowed through a flow cell where the solution will be in contact with the sensor, producing a potential change recorded as a peak. A linear calibration graph in range of 10 - 100 mg [ was obtained with a detection limit of 2 mg L-1. Relative standard deviation for 7 replicates injecting of 20, 60 and 90 mg L-1 chloride solution was 1.0,1.2 and 0.6 % respectively. Sample throughput of 60 h-1 was achieved with the consumption of 1 mL each of electrolyte solution and water carrier. The developed method was validated by the British Standard methods.
References
British Standard: Testing aggregates, Part 117: Method for determination of water soluble chloride salts (BS 812: Part 117:1988, Method A), British Standard Institution, 1988.
British Standard : Admixtures for concrete, mortar and grout - Test Methods - Part 10: Determination of water soluble chloride content (BS EN 480–10: 1997), British Standard Institution, 1997.
VAN STADEN, J. F. ands. I, TLOWANA. Spectrophotometric determination of chloride in mineral and drinking waters using sequential injection analysis. Fresenius J. Anal. Chem., 2001, 371, 396-399.
SILVA, C. R., et al. Flow injection spectrophotometric method for chloride determination in natural waters using Hg(SCN)2 immobilized in epoxy resin. Talanta, 2005, 65, 965-970.
MAYA, F., J. M, ESTELA., and V, CERDA. Spectrophotometric determination of chloride in waters using a multisyringe flow injection system. Talanta, 2008, 74, 1534-1538
MESQUITQ, R. B. R., S. M. V, FERNANDES., and A, RANGEL. Turbidimetric determination of chloride in different types of water using a single sequential injection analysis system. J. Environ. Monitor., 2002, 4, 458-461.
BONIFACIO, V. G., et al. An improved flow system for chloride determination in natural waters exploiting solid-phase reactor and long pathlength spectrophotometry. Talanta, 2007, 72, 663-667.
DA SILVA, J. E., et al. Simultaneous determination of pH, chloride and nickel in electroplating baths using sequential injection analysis. Anal. Chim. Acta., 2004, 506, 197-202.
DA SILVA, I. S., et al. FIA-potentiometry in the sub-Nernstian response region for rapid and direct chloride assays in milk and in coconut water. Talanta, 2005, 67, 651-657.
JAKMUNEE, J., L, PATIMAPORNLERT., S, SUTEERAPATARANON., N, LENGHOR., and K, GRUDPAN. Sequential injection with lab at-valve (LAV) approach for potentiometric determination of chloride. Talanta, 2005, 65, 789-793.
JUNSOMBOON, J. and J, JAKMUNEE. Determination of chloride in admixtures and aggregates for cement by a simple flow injection potentiometric system. Talanta, 2008, 76, 365–368.
FRENZEL, W. Application of flow injection potentiometry to the determination of chloride in various matrices. Fresenius J. Anal. Chem.,1989, 335, 931-937.
ALTUNBULDUK, T., H. Meier zu, KOECKER., W, FRENZEL. Studies on the elimination of sulfide interference in the potentiometric determination of chloride using ion selective electrodes in a flow injection system. Fresenius J. Anal. Chem.,1995, 351, 593-598.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Bulletin of Applied Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.









