The comparison of method of mercury determination in solid waste and leachate : A case study of mercury determination in coal fly ash from power plant and sludge from wastewater treatment plant
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.60136/bas.v5.2016.288Keywords:
Mercury, Fly ash, Mercury determinationAbstract
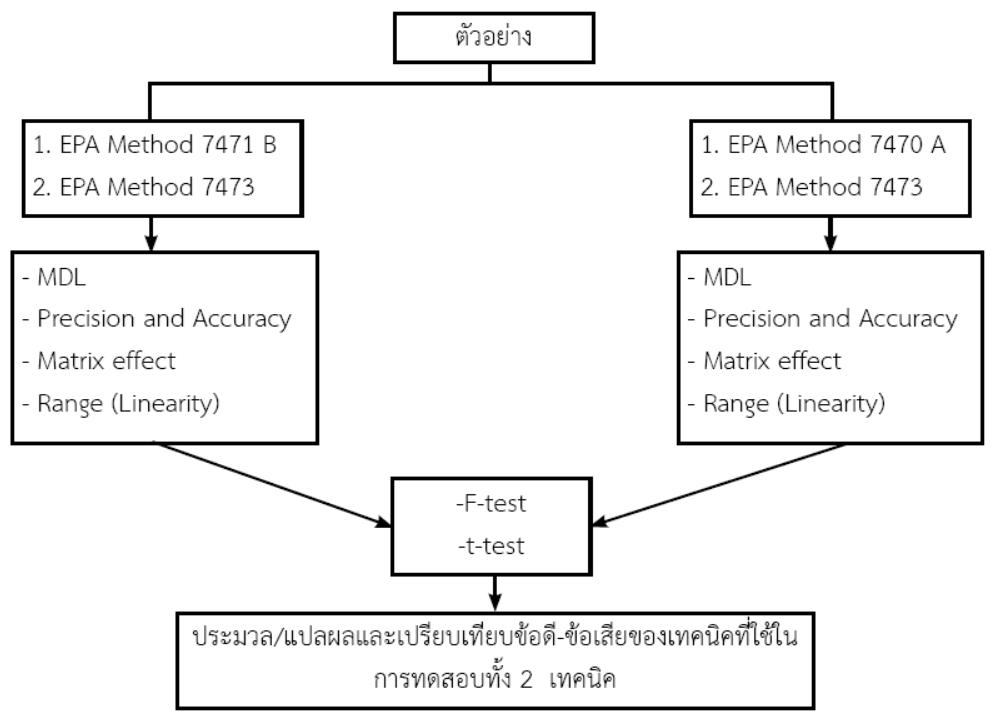
Mercury determination in the environment is really important, because of its highly toxic when contaminated in the environment. Therefore, Thai government has limited total mercury concentration in the environment in low concentration. Those concentrations are dependent on each standard for example less than 2 microgram per litter in surface water, less than milligram per cubic meter in ambient air and less than 0.200 milligram per litter in leachate. The alternatives of methods to determine low concentration mercury depend on physical property of sample and range of mercury concentration. The Environment group, Department of Science Service is not only environment testing laboratory but also the third party of testing in Thailand. Therefore, the test results must be of high precision, high accuracy and acceptance. This research focuses on comparison of test results from two methods used to determine low concentration mercury. These two methods are EPA Method 7471 B: Mercury in Solid or Semisolid Waste (Manual Cold-Vapor Technique) and EPA Method 7473 : Mercury in Solid and Solutions by Thermal Decomposition, Amalgamation, and Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometry. The reference material (mercury in sludge and mercury in fly ash) is total mercury sample while coal fly ash from power plan is a leachate sample. The test results indicated that Cold - Vapor Technique are not deference and Thermal Decomposition, Amalgamation, and Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometry. The comparison of uncertainty between Thermal Decomposition, Amalgamation, and Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometry and Cold - Vapor Technique showed that Thermal Decomposition, Amalgamation, and Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometry were less than Cold - Vapor Technique. Moreover, the volume of waste and its toxicity from Thermal Decomposition, Amalgamation, and Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometry were less than Cold - Vapor Technique.
References
กระทรวงอุตสาหกรรม. ประกาศกระทรวงอุตสาหกรรม เรื่อง การกำจัดสิ่งปฏิกูลหรือวัสดุที่ใช้แล้ว พ.ศ. 2548. ราชกิจจานุเบกษา. 2548, 123 (ตอนพิเศษ 11 ง), 14.
UNITED STATES ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION AGENCY, US EPA (2007), EPA Method 7471 B: Mercury in solid or semisolid waste (Manual cold-vapor technique), pp.11.
UNITED STATES ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION AGENCY, US EPA (2007), EPA Method 7473: Mercury in solid and solutions by thermal decomposition, amalgamation, and atomic absorption spectrophotometry, pp.17.
UNITED STATES ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION AGENCY, US EPA (1994), EPA Method 7470 A: Mercury in liquid waste (Manual cold-vapor technique), pp.6.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Bulletin of Applied Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.









