Comparison of solvent and techniques for extraction of benzophenone from paper intended to come into contact with foodstuffs
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.60136/bas.v5.2016.287Keywords:
Benzophenone, Food contact material, PaperAbstract
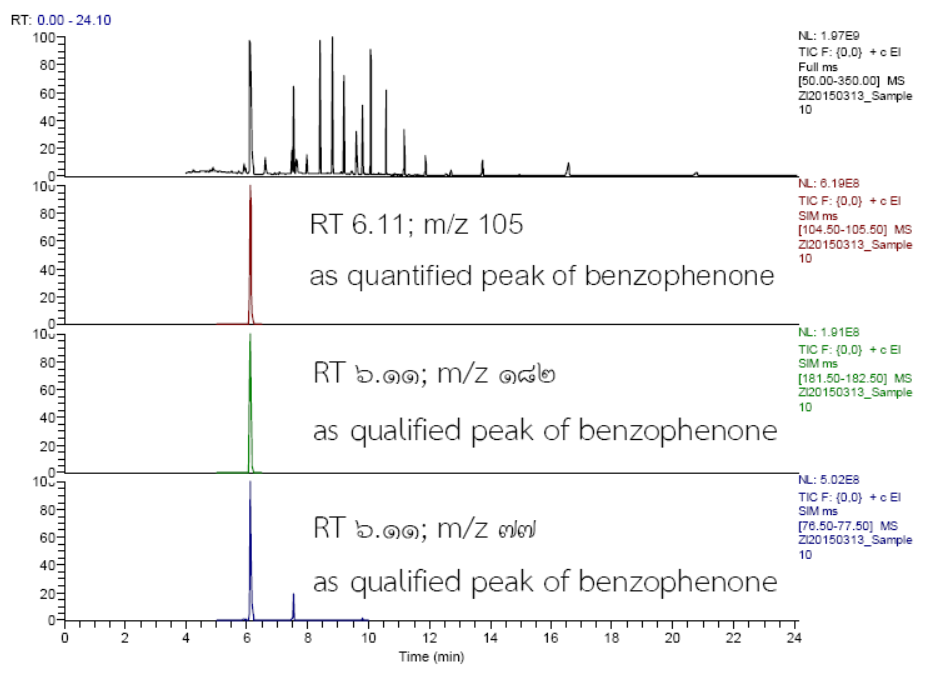
Benzophenone is used as a photo-initiator in UV cure ink for printing of packaging. Basically, colorful paper packaging may be contaminated with high concentration of benzophenone. If the paper is extracted using inappropriate method, extracted benzophenone might be less than the actual amount. Therefore, to obtain the efficiency of extraction, Chinese cake paper box contaminated with benzophenone in high concentration was selected as test sample. The sample was extracted using various solvent, including acetonitrile, ethanol and mixture of dichloromethane and three kinds of solvents, such as cyclohexane, hexane and acetronitrile in the ratio of 1:1. This study found that the extracted paper sample using 95% ethanol gave the highest yield of benzophenone. The yield form 95% ethanol extraction is around 7% higher than those from acetronitrile and acetronitrile: dichloromethane (1:1) and around 5096 yield higher than those from the mixture of dichloromethane and cyclohexane or hexane used. Furthermore, the results of extracted benzophenone by varying extraction techniques: at room temperature for 24 hr, 60°C for 2 hr in water bath and temperature below 60°C ultrasonic bath were 308, 322 and 320 mg/kg, respectively. Although these results are not significantly different at 95% confidences (One Way Anova, p = 0.397), ultrasonic extraction gave the least standard deviation (n=3). In conclusion, the appropriate technique for benzophenone extraction from food contact paper is ultrasonic extraction using 95% ethanol as extraction solvent.
References
HOECK, E. Van., et al. Analysis of benzophenone and 4-methylbenzo- phenone in breakfast cereals using ultrasonic extraction in combination with gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (GC-MSn). Analytica Chimica Acta. 2010, 633(1), 55-59.
PASTORELLI, S., et al. Study of the migration of benzophenone from printed paperboard packages to cakes through different plastic films. Eur. Food Res. Techno. 2008, 227(6), 1505-1590.
NATIONAL TOXICOLOGY PROGRAM (NTP). Toxicity Studies of Benzophenone (CAS No. 119-61-9). Administered in Feed to F344/N rats and B6C3F1 mice. Toxicol Rep. Series 2000, 1-53, A1-A13. [online]. Available from: http://ntp.niehs.nih.gov/ntp/htdocs/ST_pts/tox061.pdf.
CASTLE, L., et al. Migration studies from paper and board food packaging materials. Part 2. Survey for residues of dialkylamino benzophenone UV-cure ink photoinitiators. Food Additives and Contaminants. 1997, 14, 45-52
JOHNS, S.M., L. W., GRAMSHAW., L., CASTLE and S. M., JICKELLS. Studies on Functional Barriers to Migration 1 Transfer of Benzophenone from Printed Paperboard to Microwaves Food. Deutsche Lebensmittel-Rundschau. 1995, 91, 69-73
KOIVIKKO, R, et al. Rapid multi-analyte quantification of benzophenone, 4-methylbenzophenone and related derivatives from paperboard food packaging. Food Additives and Contaminants. 2010, 27, 1478-1486.
BRITISH STANDARD, BS EN 15519: 2007. Paper and board intended to come into contact with foodstuffs-Preparation of an organic solvent extract.
BARWICK, V.J. Strategies for solvent selection- a literature review. Trends in Analytical Chemistry. 1997, 16, 293-309.
NATIONAL TOXICOLOGY PROGRAM (NTP). Toxicity Studies of Benzophenone (CAS No. 119-61-9). Administered in Feed to F344/N rats and B6C3F1 mice. Toxicol. Rep. Series [online]. Available from: http://ntp.niehs.nih.gov/ntp/htdocs/ST_rpts/tox061.pdf
U.S. DEAPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES FOOD AND DRUG ADMINISTRATION. Guidance for Industry Q3C – Tables and List1” 2012, revision 2 [online]. Available from: http://www.fda.gov/downloads/drugs/guidancecomplianceregulatoryinformation guidances/ucm073395.pdf.
MELECCHI, M.I.S., et al. Optimization of the sonication extraction method of Hibiscus tiliaceus L. flowers. Ultranonics Sonochemistry. 2006, 13, 242-250.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Bulletin of Applied Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.









