Effect of electrostatic on weighing accuracy
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.60136/bas.v8.2019.263Keywords:
Static electricity, Weighing, Measurement accuracy, Measurement precisionAbstract
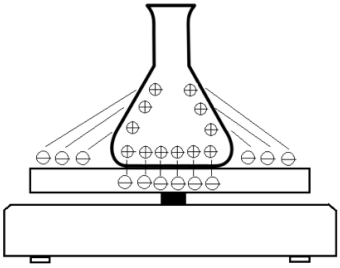
One of several parameters causing inaccuracy in precision weighing is a static electricity. The charging occurs through rubbing during the handling of objects or containers. It mostly affects insulator materials such as rubber, plastic, glass and powder. Various types of materials such as glass, plastic, aluminium, rubber, and paper are tested in this research but plastic and glass samples are easily to get charged in conformity with the triboelectric series. The charged and neutralized objects are weighed with analytical and micro balances. The charged samples have the problems with the measurement drift and the balance stability. The electrostatic charge affects the measurement accuracy as the weight value of the charged object appears heavier. This measurement error is caused by the electrostatic forces acting between the object and the balance. The charged object also gives the poorer measurement repeatability than the discharged object, as confirmed by the high standard deviation.
Therefore, the removal of the electrostatic charge or the neutralization on charged samples is essential for weighing process. This is to improve the balance stability, measurement accuracy and measurement precision. The reliable measurement results will be finally obtained.
References
Weighing the right way, proper weighing with laboratory. Greifensee, Switzerland : Mettler-Toledo AG Laboratory & Weighing Technologies, 2008. 36 p.
CROSS, J. A. Electrostatics : principles, problems and applications. Bristol, UK : IOP Publishing, 1987. 500 p.
TEXTILE CENTRE OF EXCELLENCE. Antistatic [online]. 2017. [viewed 26 April 2019]. Available from: http://www.tikp.co.uk/knowledge/material-functionality/antistatic/.
SHIMADZU EXCELLENCE IN SCIENCE. Static electricity remover for electronic balances [online]. 2013. [cited 26 April 2019]. Available from: https://www.teopal.fi/wp-content/uploads/2015/10/Stablo-Ex_ionisaattori_Shimadzu.pdf.
METTLER-TOLEDO. Electrostatic charges and their effects on weighing [online]. [cited 26 April 2019]. Available from: https://www.mt.com/nz/en/home/library/collections/laboratory-weighing/electrostatic-and-weighing.html?smartRedirectEvent=true.
GUMKOWSKI, G. and A. STEINMAN. Mitigating electrostatic effects on measurement accuracy [online]. NRD – Advanced Static Control, July 2014. [cited 26 April 2019]. Available from: https://us.vwr.com/assetsvc/asset/en_US/id/22560272/contents.
อัจฉราวรรณ วัฒนหัตถกรรม และว่าที่ ร.ต. ศักดิ์สิทธิ์ ดีอ่ำ. การพัฒนาอุปกรณ์กำจัดไฟฟ้าสถิตเพื่อลดความผิดพลาดเครื่องชั่ง. เอกสารผลงานที่เสนอขอประเมินเพื่อแต่งตั้งให้ดำรงตำแหน่งนักวิทยาศาสตร์ระดับชำนาญการพิเศษ, กรุงเทพฯ : กรมวิทยาศาสตร์บริการ. 2560.
พูลพงษ์ บุญพราหมณ์. ไฟฟ้าสถิตในงานอุตสาหกรรม. พิมพ์ครั้งที่ 1. กรุงเทพฯ : สมาคมส่งเสริมเทคโนโลยี (ไทย-ญี่ปุ่น). 2530. 168 หน้า.
SARTORIUS. Sartorius Micro : Analytical, Semi-micro- and Microbalances Installation and Operating Instructions. Goettingen, Germany : Sartorius.
NATER, R., et al. Dictionary of weighing terms : a guide to the terminology of weighing. Dordrecht, Switzerland : Springer, 2009. 269 p.
METTLER-TOLEDO. Electrostatic charges in weighing, innovative detection solution [online]. [viewed 28 August 2019]. Available from: https://www.mt.com/dam/P5/labtec/02_Analytical_Balances/10_Excellence_Line/WP_Antistatic_EN.pdf
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Bulletin of Applied Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.









