Microbiological quality of fresh-cut fruits from street vendors sold in Bangkok
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.60136/bas.v2.2013.241Keywords:
Fresh-cut fruits, Microbiological quality, Yeasts and molds, E.coli, Salmonella, Staphylococcus aureusAbstract
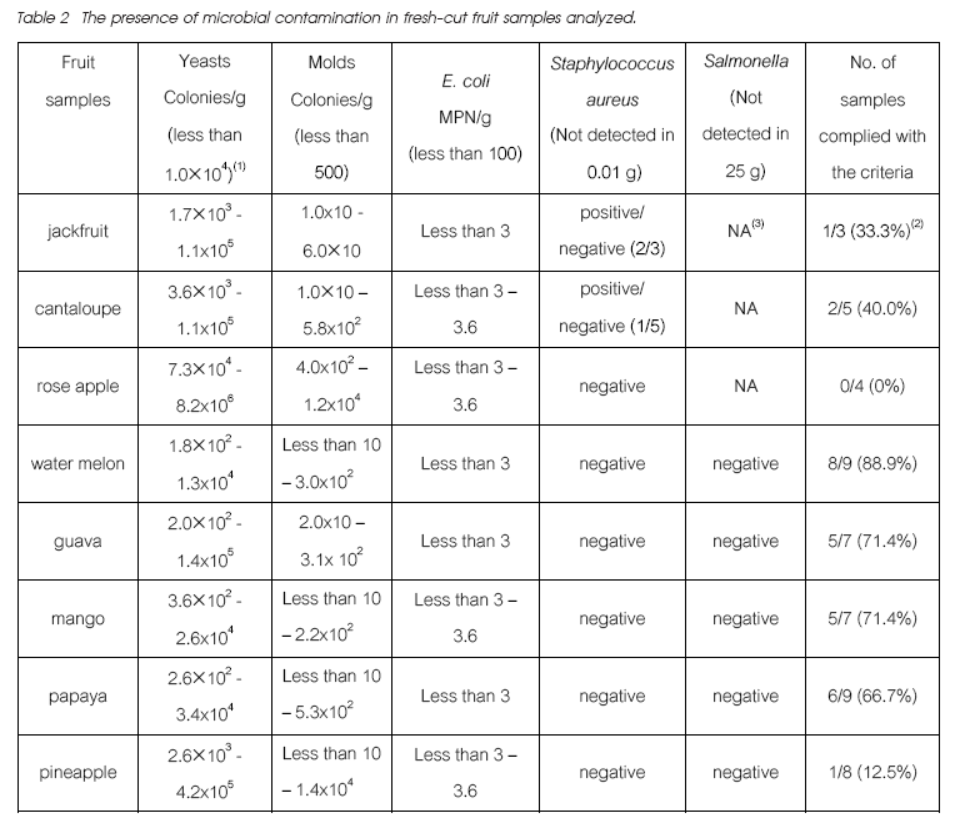
Microbiological quality evaluation of fresh-cut fruits from street vendors in Bangkok were conducted. Eight types of fruits comprised of jackfruit, cantaloupe, rose apple, water melon, guava, mango, papaya and pineapple as the total of 52 samples were collected from 3 locations. The fresh-cut fruit samples were examined for microbiological quality on the aspects of yeasts, molds, E. coli, Salmonella and Staphylococcus aureus. According to the microbiological guidelines for ready-to-eat food issued by the Department of Medical Science, it was found that 53.8% (28/52) of samples complied with the criteria. Yeasts and molds were found in every fruits samples with 38.5 % and 15.4 % of samples over the guideline criteria for yeasts and molds, respectively. For E.coli, 7% of the samples were found but below the guidelines criteria. Furthermore, for pathogenic bacteria, 7% of samples were Staphylococcus aureus positive. Salmonella was not detected. The results suggest that the risk of foodborne illness from fresh-cut fruits is high. Therefore, the sanitary quality of the processing of the produce should be concerned by applying Good Hygiene Practices (GHP) during preparation and selling. This will help controlling contamination of products and make the fruits safe for consumption.
References
นภาพร เชี่ยวชาญ. การควบคุมการปนเปื้อน จุลินทรีย์ในผักและผลไม้, วารสารจาร์พา, กรกฎาคม/ สิงหาคม, 2546, ปีที่ 10 ฉบับที่ 73, หน้า 38-41.
Fresh Produce: A Growing Cause of Outbreak of Foodborne Illness in the United States, 1973 through 1997. Journal of Food Protection, 2004, Vol 67, No.10, p.2342-2353.
แบคทีเรียในอาหาร, สำนักหอสมุดและ ศูนย์สารสนเทศ วิทยาศาสตร์และเทคโนโลยี, กรม วิทยาศาสตร์บริการ พฤษภาคม 2553.
Downes, FP., and Ito, K. Compendium of Methods for the Microbiological Examination of Foods. 4th ed. Washington, DC : Sheridan Books, Inc, 2001,p 209 -211.
FDA Bacteriological Analytical Manual online 2001. Chapter 4: Escherichia coli and the Coliform Bacteria, U.S. Food & Drug Administration, Center for Food Safety & Applied Nutrition. (online) (cited 5 April 2013). Available from Internet: http:// www.cfsan.fda.gov/~ ebam/bam-4.html.
Official methods of analysis of AOAC international. 18^ ed. AOAC Official method 975.55 Staphylococcus aureus in Foods. AOAC international, 2005, chapter 17, p.73-74.
กรมวิทยาศาสตร์การแพทย์. เกณฑ์คุณภาพ ทางจุลชีววิทยาของอาหารและภาชนะสัมผัสอาหาร. (ออนไลน์) อ้างถึงวันที่ 30 มกราคม 2554 ถึงได้จาก http://www.dmsc.moph.go.th/webroot/BQSF/file/ varity/cheme/confict.htm.
Chukwu, C. 0. C., Chukwu, I. D., Onyimba, I. A., Umoh, E. G., Olarubofin, F. and Olabode. A. O. Microbiological quality of pre-cut fruits on sale in retail outlets in Nigeria. Journal of Agricultural Research, 2010, 17: 2272-2275.
SCF/CS/FMH/SURF/Final, Risk Profile on the Microbiological Contamination of Fruits and Vegetables Eaten Raw, Report of the Scientific Committee on Food, European Commission Health & Consumer Protection Directorate-General, 29 April 2002.
Badosa, E., Trias, R., Par s, D., Pla, M., and Montesinos, E. Microbiological quality of fresh fruit and vegetable products in Catalonia (Spain) using normalised plate count methods and real time polymerase chain reaction (QPCR). Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture. 2008, 88: 605-611.
Centre for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Salmonella oranienburg gastroenteritis associated consumption of precut watermelons-Illinois. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, 1979, 28 522- 523.
Centre for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), Surveillance of food borne disease outbreaks in United States in 2006. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, 2009. 58(22) 609-615.
สุดสายชล หอมทอง และคณะ. การแพร่ กระจายของ Staphylococcus aureus ในผลไม้พร้อม บริโภคบริเวณ อำเภอเมืองชลบุรี จังหวัดชลบุรี, วิชาการ มหาวิทยาลัยอุบลราชธานี, 2554, 25 (3) : 12-18.
กรมวิทย์ฯ ตรวจพบน้ำแข็งบดปนเปื้อน เชื้อโรคมากที่สุด (ออนไลน์) สามารถเข้าถึงได้จาก http://new.goosiam.com/variety/html/0003022. html เข้าถึงข้อมูลวันที่ 3 พฤษภาคม 2556.
Barro, N., lboudo, I. and Traore, A.S. Hygienic status assessment of dishwater, utensils, hands and pieces of money in street food vending sites in Ouagadougou, Burkina Faso, African Journal, Biotechnol. 2006,5 1107-1112.
Muinde, O.K. and Kuria, E. Hygienic and sanitary practices of vendors of street foods in Nairobi, Kenya, AJFAND. 2005, 5 1-3 (6).
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2013 Bulletin of Applied Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.









