Development of salt substitute for reduction of sodium in ready to eat mushroom soup and snack foods
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.60136/bas.v7.2018.233Keywords:
Salt substitute, Low-sodium salt, Sodium-replacement saltsAbstract
The development of sodium-replacement salts or salt substitutes in this research was produced by reduced size of sodium salt (NaCl) to very small particles, 45 micron. Salt substitutes was prepared by mixing NaCl and KCI at the ratio 1:1, 1:2 and 2:1 (by weight). Sensory evaluation of salt substitute solution was conducted using Triangle test with 20 panelists and statistical tested by Chi-Square (X2). The sample of salt substitute solution test at the concentration 1% by weight, panelist could not detect the difference between control sample (Sodium salt) and salt substitute (NaCl and KCl ratio 1:1). Sensory evaluation result for the concentration 2% solution, panelist could not detect the difference between control sample and salt substitute (NaCl and KCl ratio 1:1 and 2:1), at the 95 percent confidence level (P>0.05). The sensory evaluation result shown that panelist can detect the difference of control sample and salt substitute NaCl and KCl at the ratio 1:2 (P<0.05)
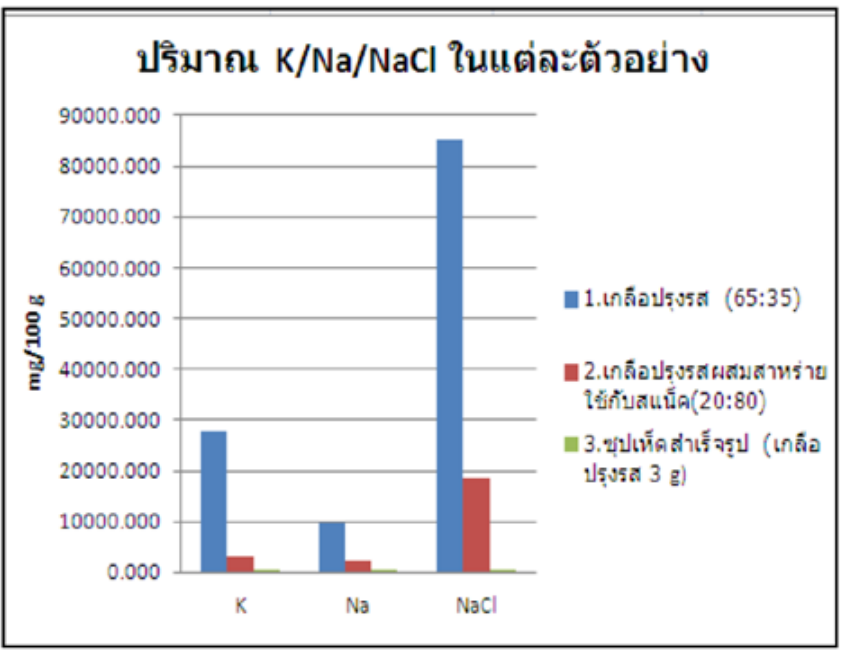
The formula development of salt substitute contained KCl and NaCl at the ratio 60:40, 65:35 and 70:30, added taurine 1%, tartaric acid 0.1% or ascorbic acid 0.1%. These salt substitutes formulas were analyzed sodium content, it has sodium 15.01-17.59 gram/100 gram. Suitable salt substitute formula contained KCl and NaCl at the ratio 65:35 added taurine 1% and ascorbic acid 0.1%, it used for Straw mushroom soup and product has sodium 32.38-35.97 milligram/one serving (150 gram), which complied with definition of very low sodium food. Salt substitute formula was tested in snack, which contained of KCl and NaCl ratio 65:35, added taurine 1%, ascorbic acid 0.1% and mix with dried seaweed. This sodium-replacement salts was used for flavoring on banana cracker. Salt substitute mixed with dried seaweed contained K 65.58 gram, Na 9.09 gram and NaCl 86.85 gram. The flavoring banana cracker with salt substitute (mixed with dried seaweed) has sodium content 131.20 mg of sodium per serving (100 gram), which complied with definition of low sodium food.
References
Health conditions-High blood Pressure (Hypertension), Low Salt Foods.com Raising Sodium Awareness [online]. [viewed 21 August 2017]. Available from: www.heart.org/HEARTORG/.../Sodium-Salt-or-Sod...
AMERICAN HEART ASSOCIATION. Sodium (Salt or Sodium Chloride) [online]. [viewed 21 August 2017]. Available from: www.heart.org/HEARTORG/.../Sodium-Salt-or-Sod...
AMERICAN HEART ASSOCIATION. Sodium and Your Health [online]. [viewed 21 August 2017]. Available from: https:// www sodium breakup.heart.org/sodium_and_your_health
U.S. FOOD AND DRUG ADMINISTRATION. Food Fact. Sodium in Your Diet: Use the Nutrition Facts Label and Reduce Your Intake [online]. [viewed 21 August 2017]. Available from: https://www.fda.gov/downloads /Food/ Ingredients PackagingLabeling/ UCM315471.pdf
STOKKERS, GERRIT JAN and EVERT ALTENA. Process to prepare a low-sodium salt product, product obtainable thereby and the use there of [online]. 2010. [viewed 21 August 2017]. Available from: https://www.google.com/ patents/ US20120045550?dq=Stokkers,+Gerrit++Jan+;+Altena, +Evert+.... US 20120045550 A1
MEYER, R. S. Low sodium salt substitute compositions. 2010 U.S. Patent: 0239740
SALEMME, FRANCIS RAYMOND, ABRAHAM I. BAKAL and RICHARD BARNDT. Compositions and methods for producing flavored seasonings that contain reduced quantities of common salt [online]. 2008. [viewed 21 August 2017] Available from: https://www.google.com/patents/US20090035444 Oct 16, 2008-US 20090035444A1.
SALEMME, F.R., BAKAL, A.I. and BARNDT, R. Composition and methods for producing flavored seasonings that contain reduced quantities of common salt. 2006. U.S. Patent: 0286275
GANESAN, K., H. ZOERB, G. MULLALLY and ADAMS WEIGLE, D.t. Ingredient systems comprising Trehalose, food products containing Trehalose, and methods of making same. 2007. U.S. Patent 0292593.
MU, J., et al. Family-based randomized trial to detect effects in blood pressure of a salt substitute containing potassium and calcium in hypertensive adolescents. American Journal of Hypertension. 2009, 22(9), 943-947.
WORLD HEALTH ORGANIZATION. Guideline: Potassium intake for adults and children [online]. 2012. [viewed 21 August 2017]. Available from: http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/75146/1/9789241548441_eng.pdf)
OJEU. 2011. Regulation (EU) No 1169/2011. Official Journal of the European Union [online]. 2011. [viewed 21 August 2017]. Available from : http:// cur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?un=CELEX:32011R1169&from =HR
CEPANEC, KATICA, et al. Potassium chloride – based salt substitutes: a critical review with a focus on the patent literature. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety. 2017, 16(5), 881-894.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Bulletin of Applied Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.









