Nitrosamines in rubber gloves used for food contact applications
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.60136/bas.v9.2020.214Keywords:
Nitrosamine, Rubber glove, Food contact rubberAbstract
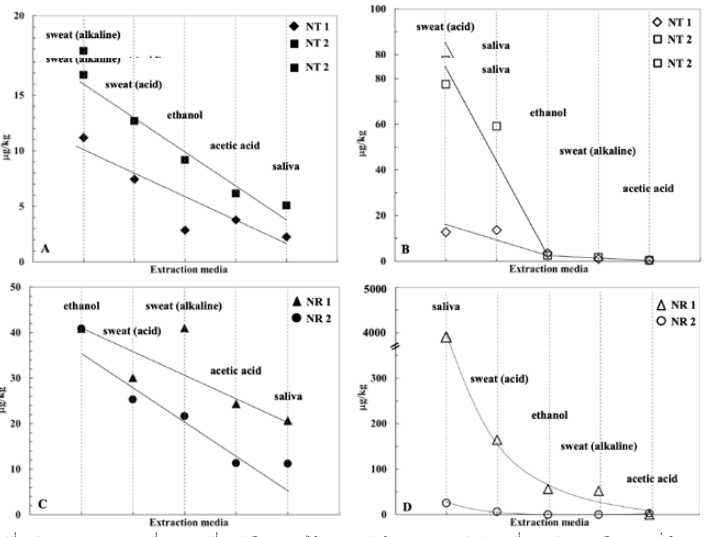
Rubber gloves are used daily in various applications including for food handling purposes. In order to assess possible exposure of the wearers to N-nitrosamines as well as possible release of N-nitrosamines to foods being contacted to these gloves, effects of extraction media are investigated. Artificial saliva, artificial sweats, and some food simulants are used for the extractions and twelve N-nitrosamines including NDMA, NDEA, NDPA, NDiBA, NDBA, NPIP, NPYR, NMOR, NEPhA, NMPhA, NDiNA, and NDBzA are analysed using GC-TEA. By using different extraction media, the levels of the released N-nitrosamines and N-nitrosatable substances are different leading to the differences in the judgement for the EU Directive compliance. By comparing with data of daily intake of N-nitrosamines from foods, the intake of N-nitrosamines migrated from gloves used for food handling under the most unfavourable circumstances could lead to an exceeding of dietary intake. It is suggested that only rubber gloves certified for selected purpose should be used for food contact application.
References
FENG, DI, et al. Detection and toxicity assessment of nitrosamines migration from latex gloves in the Chinese market. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health. 2009, 212, 533-540.
FENG, DI, et al. Evaluation of simulant migration of volatile nitrosamines from latex gloves and balloons by HS-SPME–GC–MS. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2012, 50, 733-738.
FIDDLER W, J.W. PENSABENE and W.I. KIMOTO. Investigation of volatile nitrosamines in disposable protective gloves. Am. Ind. Hyg. Assoc. J. 1985, 46(8), 463-465.
Commission Directive 93/11/EEC [online]. March, 1993. [viewed 4 March 2020]. Available from: https://eurlex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX%3A31993L0011
EUROPEAN COMMITTEE FOR STANDARDIZATION. EN 12868:2017. Child use and care articles-Methods for determining the release of N-nitrosamines and N-nitrosatable substances from elastomer or rubber teats and soothers. 2017.
INTERNATIONAL ORGANIZATION FOR STANDARDIZATION. ISO 29941:2010. Condoms-Determination of nitrosamines migrating from natural rubber latex condoms. Geneva, Switzerland: International Organization for Standardization (ISO). 2010.
EUROPEAN COMMITTEE FOR STANDARDIZATION. EN 71-12:2013. Safety of toys Part 12 : N-nitrosamines and N-nitrosatable substances. 2013.
INTERNATIONAL ORGANIZATION FOR STANDARDIZATION. ISO 105-E04:2013. Textiles - Tests for colour fastness-Part E04 Colour fastness to perspiration. Geneva, Switzerland : International Organization for Standardization (ISO). 2013.
Risk assessment of N-nitrosamines in balloon [online]. April, 2002. [viewed 4 March 2020]. Available from: https://mobil.bfr.bund.de/cm/349/risk_assessment_of_n_nitrosamines_in_balloons.pdf
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Bulletin of Applied Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.









