Vibration effect on laboratory balance with different readability and loading
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.60136/bas.v6.2017.199Abstract
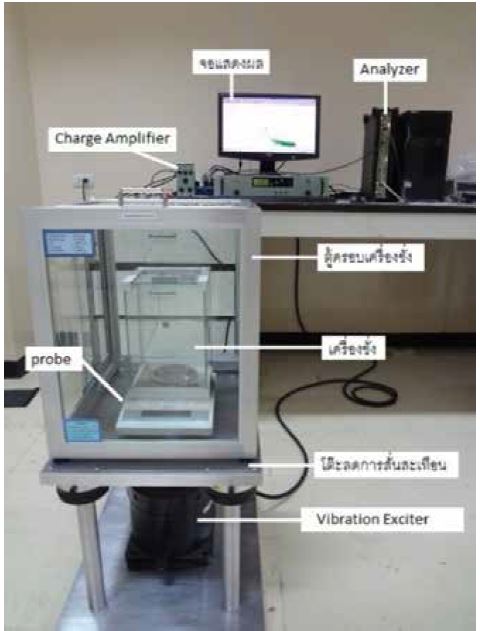
This research is aimed to find the vibration effect on the performance of laboratory balances with different readability and loading in order to propose the guideline for installing the balance in the environment avoiding the vibration effect for ultimate performance. The balances with different readability 0.01 g, 0.001 g, 0.0001 g, 0.00001 g, 0.000001 g and different loading value are investigated. The experimental setup is consisted of the anti-vibration table for installing the balance in order to exclude the vibration from the floor, the exciter used to generate the vibration, and the accelerometer used for detecting the vibration signal. The natural frequency (Hz) of the balance system and the amplitude of vibration which effect to the reading performance of the balances are measured. The results show that most balances (different readability) response to the high frequency (> 400 Hz) except the balance with 0.01 g readability that the natural frequency is 30 Hz which is low frequency the same as the source of vibration in the laboratory; motor of the air-conditioner ~30 Hz to 50 Hz. The amplitude of vibration is in the range of 0.3 m/s to 0.7 m/s. Furthermore, the natural frequency of most balances are the same or slightly different at different loading in the range of maximum capacity. Therefore, the loading value is insignificant effect to the natural frequency of the balance system.
References
STANESCU, M. and CA. MICU. Influencing factors for the measuring results. Error sources and some possibilities to reduce for those errors. Fascicle of Management and Technological Engineering. 2008, VII(XVII), 1077-1084.
WEYHE, S. Weighing Technology in the Laboratory: Technology and Applications. Goettingen: Sartorius, 1997, pp. 12-13.
SCHWARTZ, R., M. BORYS and F. SCHOLZ. PTB-MA-80e: Guide to mass determination with high accuracy. Braunschweig: PTB, 2007, pp. 25, 34-35.
MORRIS, EC. and KMK, FEN. The Calibration of Weights and Balances. Sydney: CSIRO, 2003, pp. 115.
GLÄSER, M. PTB-MA-52: Advices for the calibration of mass standards. Braunschweig: PTB, 1997, pp. 22.
BRITISH STANDARDS INSTITUTION. Metallic materials - Vickers hardness test: Calibration of reference blocks. BS 6507 Part 3. 2005, pp. 4.
SANPONPUTE, T. and A. MEESAPLAK. Vibration effect on Vickers hardness measurement. IMEKO 2010 TC3, TC5 and TC22 Conferences Metrology in Modern Context, November, 2010, pp. 145-149.
SANPONPUTE, T. and A. MEESAPLAK. Vibration effect on Rockwell scale hardness measurement. XIX IMEKO World Congress Fundamental and Applied Metrology, September, 2009, pp. 1006-1010.
UNITED KINGDOM ACCREDITATION SERVICE. Calibration of Weighing Machines. UKAS LAB14. 2015.
Non- automatic weighing instrument, Part 1: Metrology and technical requirements - Test, ОIML R 76-1.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Bulletin of Applied Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.









