The effect of solvent on antimicrobial activity of medicinal plant extraction
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.60136/bas.v1.2012.183Keywords:
Antimicrobial activity, Medicinal plant Extraction, SolventAbstract
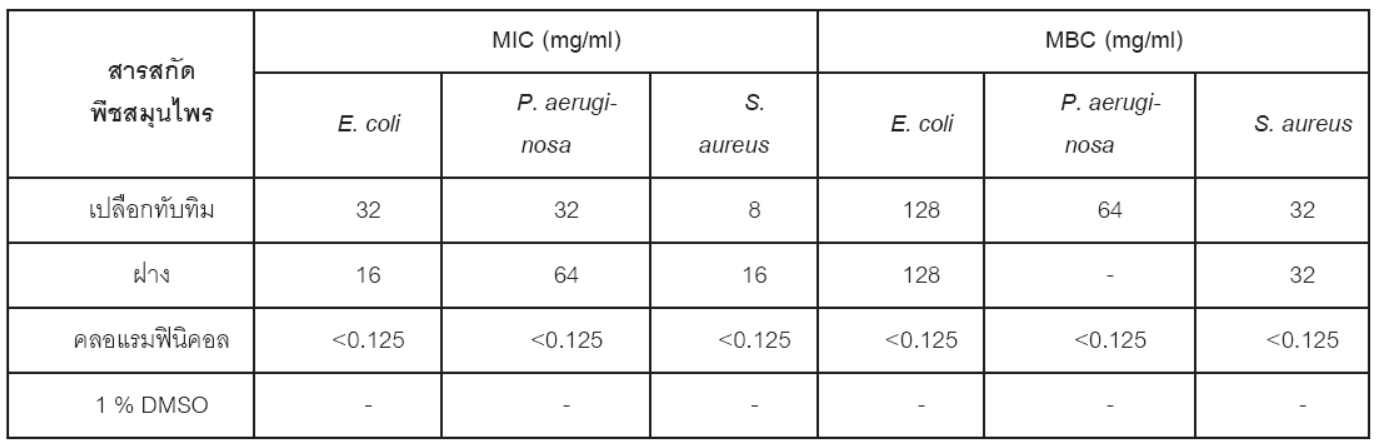
Antimicrobial activity against Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus), Escherichia coli (E.coli) and Pseudomonas aeruginosa (P. aeruginosa) of aqueous and ethanol extracts of Hibicus sabdariffa Linn., Anaxagorea luzonensis A. Gray, Betula alnoides Buch.-Ham Ex G. Don, Dracaena conferta Ridl. Plumbago rosea Linn., Punica granatum Linn. and Caesalpnia sappan Linn. were investigated. The antimicrobial activity of aqueous and ethanol extracts was determined by agar well diffusion method. The results showed that ethanol extracts were more active than the aqueous extracts except for the aqueous extract of Hibicus sabdariffa Linn. that the aqueous extract was more active. The ethanol extract of Punica granatum Linn. has shown highest antimicrobial activity compared to other extracts. The ethanol extract of Punica granatum Linn. was found to inhibit E. coli, P. aeruginosa and S. aureus with the inhibition zone of 13.02 ± 0.87, 8.14 ± 0.80 and 20.90 ± 0.05 mm, respectively. Furthermore, the extract of Punica granatum Linn. were tested for the Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) using three tested organisms and showed the MICs of E. coli, P. aeruginosa and S. aureus were 32, 32 and 8 mg/ml, respectively. The same plant extracts were also tested for the Minimum Bactericidal Concentration (MBC), which were 128, 64 and 8 mg/ml, respectively.
References
กฤษณ์ ถิรพันธุ์เมธี. 2553, “อันตรายจากแบคทีเรียจำเพาะที่ไม่ควรพบในผลิตภัณฑ์สมุนไพร” ในการควบคุมคุณภาพในการผลิตผลิตภัณฑ์สมุนไพรและเภสัชภัณฑ์, จาตุรงค์ ประเทืองเดชกุล (บรรณาธิการ), พิมพ์ครั้งที่ 1 ภาควิชาจุลชีววิทยา คณะเภสัชศาสตร์ มหาวิทยาลัยมหิดล, กรุงเทพฯ, หน้า 79-81.
ธีรพัฒน์ เวชชประสิทธิ์. เชื้อแบคทีเรีย E. coli รอบรู้วิทย์. 2554. [ออนไลน์]. [อ้างถึงวันที่ 24 เมษายน 2555]. เข้าถึงได้จาก http://magazine.ipst.ac.th/index.php/new-magazine/.../38-new3magazine?
ธีรพรรณ ภูมิภมร และอุไม บิลหมัด. การดื้อยาของเชื้อ Staphylococcus aureus ในเนื้อสุกรจากโรงฆ่าสัตว์ในภาคใต้ระหว่างปี พ.ศ. 2549-2551 วารสารสถาบันสุขภาพสัตว์แห่งชาติ, 2011, 6 (1), 1-8.
นิติพงษ์ ศริริวงศ์ และเอกชัย ชูเกียรติโรจน์. การดื้อยาปฏิชีวนะของ Staphylococcus aureus และแนวทางการควบคุม. สงขลานครินทร์เวชสาร. 2552, 27 (4), 347-358.
รัตนา อินทรานุปกรณ์, การตรวจสอบและการสกัดแยกสารสำคัญจากสมุนไพร, 2550. พิมพ์ครั้งที่ 2. สำนักพิมพ์แห่ง จุฬาลงกรณ์มหาวิทยาลัย, หน้า 83-85.
วิสาตรี คงเจริญสุนทร จินตนา จิรถาวร และวิภาพร ใจเกื้อ การศึกษาผลของสารสกัดจากสมุนไพรต่อเยื่อหุ้มเซลล์ของ แบคทีเรียสายพันธุ์ดื้อยาโดยวิธี Flow cytometry. วารสารวิทยาศาสตร์บูรพา, 2550, 12 (2), 7-9.
Jeeraporn, S., Nattapon K., Weerawan, N. and Monthon L. “Anti- Candida albicans activity of active substances derived from Morinda citrifolia fruit”. Journal of Medical Technology and Physical Therapy. 2011, 23 (1), 8-18.
Parekh J., Jadeja D. and Chanda S. “Efficacy of Aqueous and Methanol Extracts of Some Medicinal Plants for Potential Antibacterial Activity" Turk. J. Biol., 2005, 29, 203-210.
Vudhivanich, S. and S. Supanuntorn. 2002. “Potential of Thai herbal extract for growth inhibition of Ralstonia solanacearum, the causal agent of bacterial wilt of tomato. the first International Conference on Tropical and Subtropical Plant Diseases. November 5-8, 2002. Chiang Mai, Thailand. P.161.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2012 Bulletin of Applied Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.









