Synthesis of Highly Porous Materials from Industrial Waste Using Adsorbent
Main Article Content
Abstract
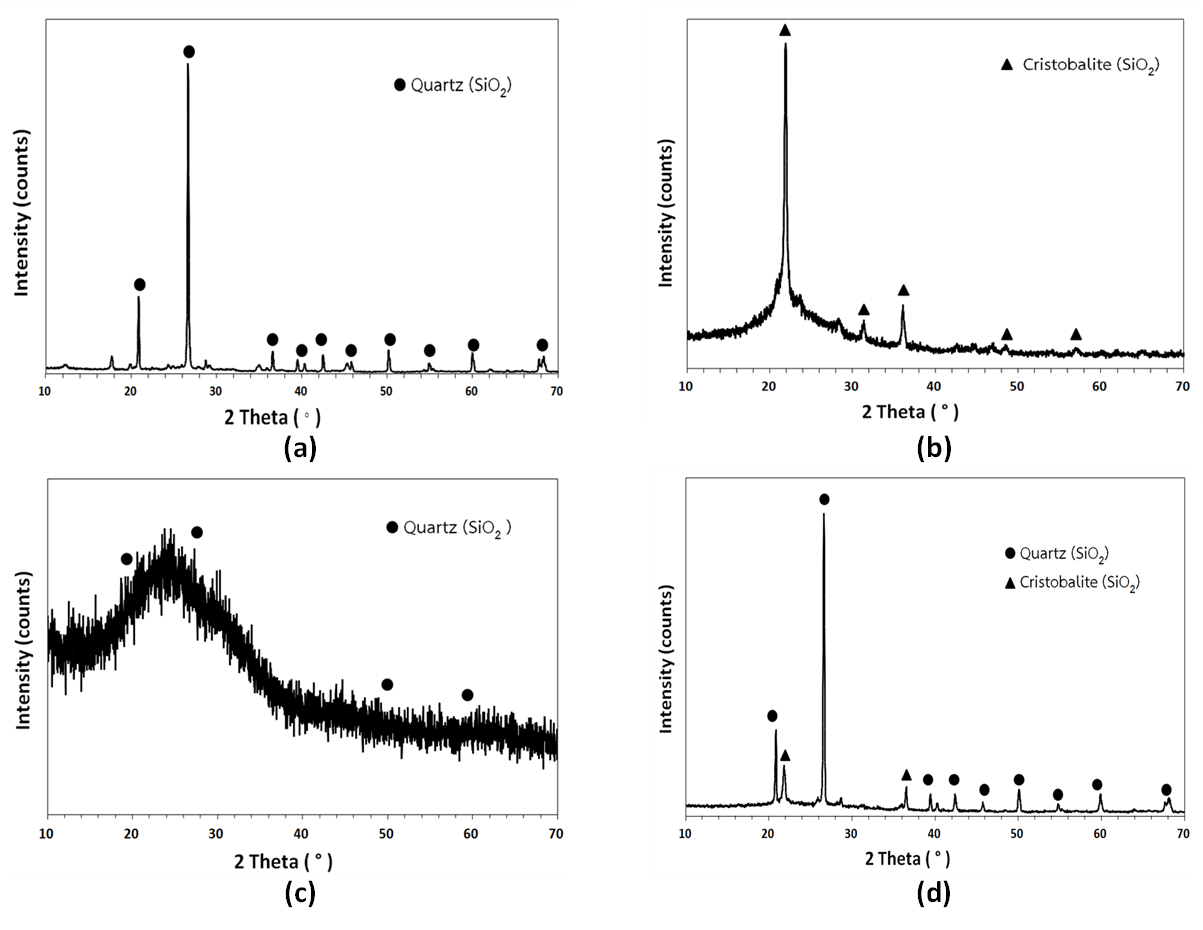
Highly porous materials from industrial waste with rations of perlite, rice husk, and waste glass, 60:20:20, 60:30:10, and 60:10:30 wt% were burnt at a temperature of 1160°C. The highly porous materials of phase structure, density, water absorption, strength and microstructure were studied. It was found that the highly porous materials with the ratio of perlite, rice husk, and waste glass that was 60:30:10 wt% showed the optimum properties for adsorbent. The phase structure showed SiO2 in a quartz form and in a cristobalite form. The highly porous materials inhibited the highest water adsorption of 28.61%. The density and strength of the highly porous materials showed 1434.56 kg/m3 and 1379.60 N, respectively, especially, the presence of the small and continuous pore sizes in structure uniform compared to the other ratios. As a result, the highly porous materials can be synthesized with industrial waste. Besides, it is an alternative for increasing the value of waste.
Article Details
References
อรอนงค์ จุลพันธ์, ธงไทย วิฑูรย์ และเมตตา เจริญพานิช. (2554). การผลิตวัสดุดูดซับชนิดซิลิกาเมโซพอร์จากกากของเสียจากธรรมชาติ. วิศวกรรมสาร มก. 24(75). 103-120.
Afroze S., and Sen T.K. (2018). A review on heavy metal ions and dye adsorption from water by agricultural solid waste adsorbents. Water, Air and Soil Pollution, 229, 225(2018). doi: 10.1007/s11270-018-3869-z.
Ahmad J., Martínez-García R., de-Prado-Gil J., Irshad K., El-Shorbagy M.A., Fediuk R., and Vatin N.I. (2022). Concrete with partial substitution of waste glass and recycled concrete aggregate. Materials, 15(2), 430. doi: 10.33 90/ma15020430.
Bartolomeu M., Neves M., Faustino M., and Almeida A. (2018). Wastewater chemical contaminants: Remediation by advanced oxidation processes. Photochemical & Photobiological Sciences, 17, 1573-1598. doi: 10.103 9/c8pp00249e.
Du J., Ma A., Wang X., and Zheng X. (2023). Review of the preparation and application of porous materials for typical coal-based solid waste. Materials, 16, 5434. doi: 10.33 90/ma16155434.
Gopinath, K.P., Vo D.V., Prakash D.G., Joseph A., Viswanathan S., and Arun J. (2021). Environmental applications of carbon-based materials: A review. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 19, 557-582. doi: 10.1007/s10311-020-01084-9.
Hameed A. Alharbi A., Abdelrahman E., Mabrouk E., Hegazey R., Algethami E., Al-Ghamdi Y.O., and Youssef H.M. (2020). Facile hydrothermal fabrication of analcime and zeolite X for efficient removal of Cd(II) ions from aqueous media and polluted water. Journal of Inorganic and Organometallic Polymers and Materials, 30, 4117-4128. doi: 10.1007/s10904-020-01565-y.
Han L., Song J., Zhang Q., Liu T., Luo Z., and Lu A. (2018). Synthesis, structure and properties of MgO-Al2O3-SiO2-B2O3 transparent glass-ceramics. Silicon, 10, 2685–2693. doi: 10.1007/s12633-018-9806-3.
Haque A.N.M.A., Sultana N., Sayem A.S.M., and Smriti S.A. (2022). Sustainable adsorbents from plant-derived agricultural wastes for anionic dye removal: A review. Sustainability, 14(17), 11098. doi: 10.3390/su141711098.
Inan S., Kusumkar V.V., Galamboš M., Viglašová E., Rosskopfová O., and Da no M. (2022). Isotherm, kinetic, and selectivity studies for the removal of 133Ba and 137Cs from aqueous solution using turkish perlite. Materials, 15(21), 7816. doi: 10.3390/ma15217816.
Jiang Z., and Hu D. (2019). Molecular mechanism of anionic dyes adsorption on cationized rice husk cellulose from agriculture wastes. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 276, 105-114. doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2018.11.153.
Makrygiannis I., and Tsetsekou A. (2022). Effect of expanded perlite in the brick mixture on the physicochemical and thermal properties of the final products. Journal of Composites Science, 6(7), 211. doi: 10.33 90/jcs6070211.
Mishra D.P., and Das S.K., (2010). A study of physico-chemical and mineralogical properties of talcher coal fly ash for stowing in underground coal mines. Materials Characterization, 61(11), 1252-1259. doi: 10.1016/j.matchar. 2010.08.008.
Naef. A., Qasem A., Ramy H.M., and Dahiru U.L. (2021). Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewater: A comprehensive and critical review. Clean Water. 4, 36. doi:10.1038/s41545-021-00127-0.
Oenema J., Harmel J., Velez R., Meijerink M., Eijsvogel W., Poursaeidesfahani A., Vlugt T.J., Zecevic J., and Jong K.P. (2020). Infulence of nanoscale intimacy and zeolite micropore size on the performance of bifunctional catalysts for n-heptane hydroisomerization. ACS Catalysis, 10(23), 14245-14257. doi: 10.1021/acscatal.0c03138.
Rad L.R., and Anbia M. (2021). Zeolite-based composites for the adsorption of toxic matters from water: A review. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 9(5), 106088. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2021.106088.
Sahoo M., and Kale P. (2019). Restructured porous silicon for photovoltaic: A review. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 289, 109619. doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2019.109619.
Sen T.K. (2017). Air, gas and water pollution control using industrial and agricultural solid wastes adsorbents (1 Ed.). New York: .CRC-Press/Taylor & Francis.
Shi Y., Qian M., Wang X., Zhang W., Zhang X., and Wang X., Zhu Y. (2022). Effect of rice husk-based silica on the friction properties of high density polyethylene composites. Materials, 15(9), 3191. doi: 10.3390/ma15093191.
Stackelberg P.E., Furlong E.T., Meyer M.T., Zaugg S.D., Henderson A.K., and Reissman D.B. (2004). Persistence of pharmaceutical compounds and other organic wastewater contaminants in a conventional drinking-water-treatment plant. Science of The Total Environment, 329(1-3), 99-113. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2004.03.015.
Sud D., Mahajan G., and Kaur M.P. (2008). Agriculture waste material as potential adsorbent for sequestering heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions-A review. Bioresource Technology, 99(14), 6017-6027. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech. 2007.11.064.
Sun Z., Li M., and Zhou Y. (2014). Recent progress on synthesis, multi-scale structure, and properties of Y-Si-O oxides. International Materials Reviews, 59(7), 357. doi:10.1179/1743280414Y.0000000033.
Xu X., Li Q., Cui H., Pang J., Sun L., An H., and Zhai J. (2011). Adsorption of fluoride from aqueous solution on magnesia-loaded fly ash cenospheres. Desalination, 272(1-3), 233-239. doi: 10.1016/j.desal.2011.01.028.
Younas F., Mustafa A., Farooqi Z.U.R., Wang X., Younas S., Mohy-Ud-Din W., Hameed M.A., Abrar M.M., Maitlo A.A., Noreen S., and Hussain M.M. (2021). Current and emerging adsorbent technologies for wastewater treatment: Trends, limitations and environmental implications. Water, 13(2), 215. doi: 10.3390/w13020215.
Yu Y., Guo D., and Fang J. (2015). Synthesis of silica aerogel microspheres by a two-step acid-base sol-gel reaction with emulsification technique. Journal of Porous Materials, 22, 621-628. doi: 10.1007/s10934-015-9934-8.