Factors Affecting Musculoskeletal Disorders in Silk Preparation Process Workers in the Silk Weaving Profession in Buriram Province
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.14456/nujst.2023.36Keywords:
Musculoskeletal disorders, Silk preparation, ErgonomicsAbstract
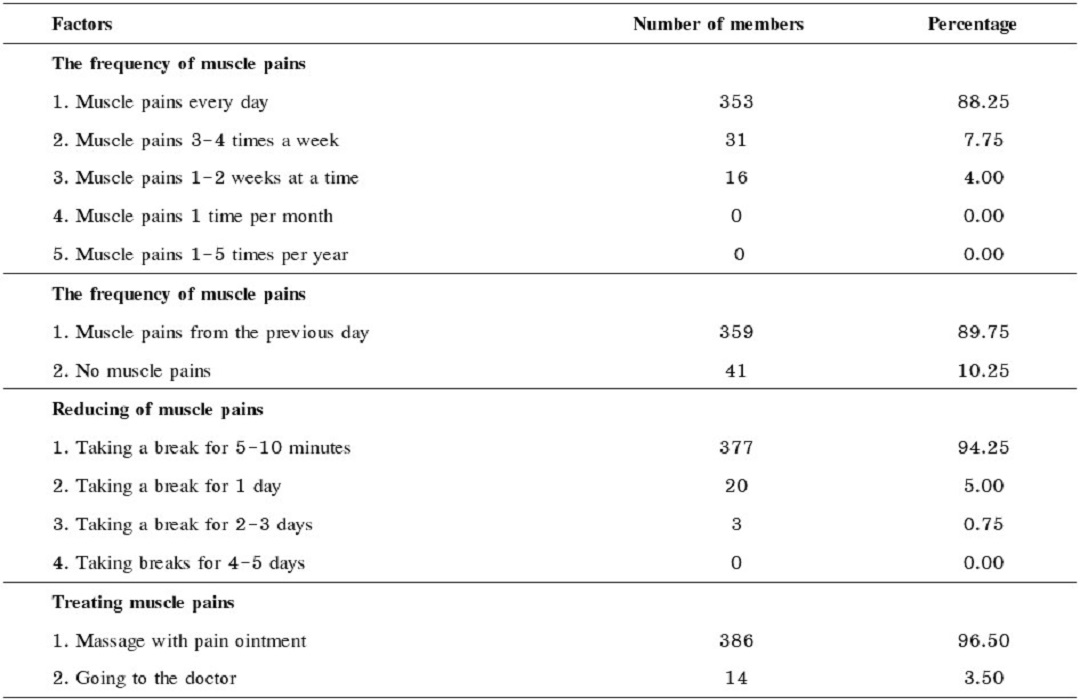
Musculoskeletal disorders in workers of the silk weaving professions have become a significant problem affecting production effectiveness. The objectives of this study were to explore the prevalence rate and factors affecting the musculoskeletal disorders of 400 female silk preparation process workers in the silk weaving profession in Buriram province. The data was collected by using questionnaires derived from the standardized Nordic questionnaire and the musculoskeletal disorders evaluation form developed by the Department of Disease Control, Ministry of Health, Thailand. The data were analyzed by descriptive statistics and binary logistic regression. The results revealed that 92% of the silk preparation professionals had problems with muscle pains mainly in their lower back and 91.75% had knees pain. Buttock and hip pain were experienced by 90.50% of the workers, and 90.25% had left and right shoulder pain. Factors affecting the musculoskeletal disorders were: 1) age, 2) working time, 3) break time, 4) reaching above the shoulder to pick up or hold the material, 5) continuous bending down of their heads to work, 6) hands or arms working in repetitive movements (for at least 30 minutes). Thus, this study identifies factors affecting MSDs among workers and gains a greater understanding of working posture according to ergonomics which may help in maintaining the health and safety of workers, and hence leading to increased work productivity and efficiency.
References
Ahmad, S., Parashar P., Bansal, R., Shrivastava, A., Shyam, S., & Kaur, G. (2013). Musculoskeletal disorders and respiratory illness of workers in small scale textile industries in Meerut District. Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Health Sciences, 3(4), 882-886.
Announcement of the Department of Labor Protection and Welfare regarding noise level standards that employees are allowed to receive on average throughout the working period each day. (2018, 26 January). Royal Gazette, Volume 135, special section 19 D., p. 15.
Announcement of the Ministry of Labor on determining the weight rate that employers can allow employees. (2004, 10 June). Royal Gazette, Volume 121, special section 35 A., p. 15.
Balasundaram, K., Ashenafi, A., Ashok Kumar, A., & Senthil Kumar, M. S. (2017). Improvement of Ergonomic Factors in a Textile Industry: A case study. Journal of Recent Research in Engineering and Technology, 4(5), 24-30.
Bernard, B. P., (2020, January 18). Musculoskeletal disorder and workplace factor: Critical review of epidemiology evidence for work-related musculoskeletal disorder of the neck, upper extremity and low back. Retrieved from http://www.cdc.gov/niosh/ 97-141pd.html
Boontha, K., Pirunsan, U., & Khamwong, P. (2016). Cardiovascular response and energy expenditure of a novel heart rate maximizer test in healthy volunteers. Journal of Associated Medical Sciences, 49(2), 263-275.
Borg, M., Bi, P., Nitschke, M., & McDonald, S. (2017). The impact of daily temperature on renal disease incidence: an ecological study. Environ Health, 16(1), 114. http:dx.doi.org/10.1186/ s12940-017-0331-4
Boyce, P. (2014). Human Factors in Lighting (3rd ed.). Boca Raton: CRC Press.
Bunchu, S., & Rakphong, N. (2012). Wisdom of Isan Indigenous Thai Silk Yarn. Bangkok: Department of Sericulture, Ministry of Agriculture and Cooperatives.
Chantaramanee, N., Taptagaporn, S., & Piriyaprasarth, P. (2014). Work-Related Musculoskeletal Problems of Hand Loom Weaving Group in Northern Thailand. Journal of Safety and Health, 7(24), 29-40.
Cook, C., & Burgess-Limerick, R. (2004). The effect of forearm support on musculoskeletal discomfort during call centre work. Applied Ergonomics, 35(4), 337-342. http:dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.apergo.2004.03.005
Department of Disease Control, Ministry of Health, & Thailand. (2017). Situation of diseases and health hazards from occupational and environment Year 2017. Nonthaburi: Ministry of Health.
Europe PMC Funders Group. (2013). Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 301 acute and chronic diseases and injuries in 188 countries. 1990–2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013, 386(9995), 717-828.
Glaser, J., Lemery, J., & Rajagopalan, B. (2016), Climate Change and the Emergent Epidemic of CKD from Heat Stress in Rural Communities: The Case for Heat Stress Nephropathy. Clinical Journal of the American Society of Nephrology, 11(8), 1472-1483. http:dx.doi.org/10.2215/CJN.13841215
Goel, K., Ahmad, S., Parashar, P., Bansal, R., Pant, B., & Goel, P. (2013). Health status and treatment seeking behaviour among power loom workers in an urban slum of Meerut city in U.P. journal of Advance Researches in Biological Sciences, 5(1), 302-305.
Heneweer, H., Staes, F., Aufdemkampe, G., van Rijn, M., & Vanhees, L. (2011). Physical activity and low back pain: a systematic review of recent literature. European Spine Journal, 6, 826-845.
Horie, S. (2013). Prevention of heat stress disorders in the workplace, Journal of the Medical Association of Thailand, 56, 186-192.
Integrated Provincial Group Management Committee Lower Northeast Provinces 1. (2019). Lower Northeastern Province Development Group Plan 1 (2018-2021). Revised Edition Year 2019, pp. 86-87.
Ivy, A. C. (1994). What is normal or normality? Quarterly Bulletin of the Northwestern University Medical School, 18, 22–32.
Jang, T. W., Koo, J. W., Know, S. C., & Song, J. (2014). Work-related musculoskeletal diseases and the workers compensation. Journal of Korean Medical Science, 29, 18-23.
Kuorinka, I., Jonsson, B., Kilbom, A., Vinterberg, H., Biering-Sørensen, F., Andersson, G., & Jørgensen, K. (1987). Standardised Nordic Questionnaires for the Analysis of Musculoskeletal Symptoms. Applied Ergonomics, 18(3), 233-237. http:dx.doi.org/10.1016/0003-870(87)90010-X
Massaccesi, M., Pagnotta, A., Soccetti, A., Masali, M., Masiero, C., & Greco, F. (2003). Investigation of work-related disorders in truck drivers using RULA method. Applied ergonomics, 34(4), 303-307. http:dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0003-6870(03)00052-8
Meenaxi, T., & Sudha, B. (2012). Causes of Musculo-Skeletal Disorder in Textile Industry. International Research Journal of Social Sciences, 1(4), 48-50.
Ministerial regulations set standards for safety management and operations. Occupational health and working environment regarding heat Light and Noise. (2016). Publishing. The Government Gazette 2016, 133(91), 47-49.
Naz, H., Kwatra, S., & Ojha, P. (2015). Prevalence of musculoskeletal disorders among handloom weavers of Uttarakhand: an ergonomic study. Journal of Applied and Natural Science, 7(1), 102-105.
Parimalam, P., Kamalamma, N., & Ganguli, A.K. (2006). Ergonomic intervention to improve work environment in garment manufacturing units. Indian Journal of Occupational and Environmental Medicine, 10(2), 20-27.
Punnett, L., & Wegman, D. H. (2004). Work-related musculoskeletal disorders: the epidemiologic evidence and the debate. Journal of Electromyography and Kinesiology, 14(1), 13-23.
Rea, M. (2013). Value metrics for better lighting (SPIE Press monograph; PM228). Bellingham, Washington: SPIE Press monograph.
Rithinyo, M. (2017). Factors affecting the production efficiency of the community Enterprise Silk in Nakhonratchasima province. Engineering Journal Chiang Mai University, 24, 180-193.
Rithinyo, M., Loatong, P., & Noyming, S. (2022). Musculoskeletal Disorders in Workers of the Silk Weaving Preparation Process: A Study Case of Surin Province, Thailand. The Journal of King Mongkut's University of Technology North Bangkok, 32(3), 647-658.
Rithinyo, M., Loatong, P., Maichum, K., & Parichatnon, S. (2022). Workstation improvement to reduce muscle aches during silk degumming and dyeing in silk weaving profession in Nakhon Ratchasima province. Engineering and Applied Science Research, 49(1), 112-118.
Rithinyo, M., Mayai, A., & Loatong, P. (2020). Factors affecting musculoskeletal disorders of workers in the silk weaving professions in Chaiyaphum province. Journal of Science & Technology MSU, 39(4), 438-445.
Saha, T. K., Dasgupta, A., Butt, A., & Chattopadhyay, O. (2010). Health status of workers engaged in the small-scale garment industry: How healthy are they. Indian Journal of Community Medicine, 35(1), 179-182.
Saruda, J. (2020). Lighting and human behavior. PSRU Journal of Science and Technology, 5(1), 13-22.
Simachokedee, W., & Chaikul, K.(1997). Ergonomics: Science of working conditions for productivity and safety (2nd ed.). Bangkok: Technology Promotion Association (Thai-Japanese).
Subramaniya Bharathy, R., & Jothi, S. (2017). A study on influence of physical related factors on performance of handloom weavers in Omalur Region, Salem Dist. Tamil Nadu, India. International Journal of Multidisciplinary Research and Development Online, 4(4), 196-200.
Thitima, N., Napapit, C., & Sirisin, C. h. (2019). Associated factor of low back pain in personnel’s of somdet chaopraya institute of psychiatry. Journal of Somdet Chaopraya Institute of Psychiatry, 13(1), 21-33.
Van den Berg, T. I. J., Elders, L. A. M., de Zwart, B. C. H., & Burdorf, A. (2009). The effects of work-related and individual factors on the work ability index: a systematic review. Occupational and Environmental Medicine, 66(4), 211-220.
Violante, F., Armstrong, T., & Kilbom, A. (2000). Occupational ergonomics work-related musculoskeletal disorders of the upper limb and back. London & New York: Taylor &Francis.
Wu, Y., Schwebel, D. C., & Hu, G. (2018). Disparities in unintentional occupational injury mortality between high-income countries and low and middle-income countries: 1990-2016. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 15(10), 2094-3002.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Naresuan University Journal: Science and Technology (NUJST)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.













